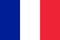
The hip joint is arthrosis (deforming arthrosis, coxarthosis, osteoarthosis) is a slowly progressive degenerative-dynist disease that over time leads to restrictions on the affected joint, lasting pain and restrictive mobility.
The disease affects people under the age of 40, and women are repeatedly ill than men.
In the general structure of arthrosis, the arthrosis of the hip joint belongs to the leading role.This is due to the widespread congenital pathology of the hip joints (dysplasia) and the significant physical exertion to which these joints are prone to.
Risk factors and causes of hip arthrosis
The main role in the abnormal mechanism of the formation of hip arthrosis is a change in the physico-chemical characteristics of synovial (intraarticular) fluid, which results in denser and viscous.This exacerbates its lubricating properties.During the movement, the articular cartilage surfaces begin to rub and become coarse, covered with cracks.The small particles of the hyaline cartilage are left and fall into the arthritis, which causes the development of aseptic (non -infectious) inflammation.As the inflammatory process of the disease, the bone tissue is involved in the inflammatory process, which leads to aseptic necrosis of the femoral head sections and the surface of the acetabulum, resulting in the formation of osteophytes (bone growth), increasing inflammation and severe pain during movement.
In the late degree of arthrosis of the hip joint, inflammation is also thrown into the surrounding joint of the tissues (blood vessels, nerves, leagues, muscles), leading to the appearance of periarthritis.As a result, the hip joint is completely destroyed, its functions are lost and the movement ceases.This condition is called ankylosis.
Causes of hip arthrosis:
- The congenital lips of the thighs;
- Hip dysplasia;
- aseptic necrosis of the femur's head;
- Peters disease;
- Hip joint injuries;
- The hip joint is infectious arthritis;
- gonarthrosis (deformation of osteoarthosis of the knee joint);
- osteochondrosis;
- Overweight;
- Professional sport;
- flat foot;
- curvature of the spine;
- Sitting lifestyle.
The pathology is not inherited, but the child inherits the properties of the structure of the muscle bone from his parents, which can cause arthrosis of the hip joint under such circumstances.This explains the fact of the existence of families, which are higher than in the population.
The forms of illness
Depending on the etiology, arthrosis of the hip joint is divided into primary and secondary.Secondary arthrosis develops in the background of other diseases or injuries of the hip joint.The primary form is not related to the previous pathology, and the cause of its development is often not possible, in which case idiopathic arthrosis is spoken.
Coksartrosis is one- or bilateral.
Stage
Three stages (degrees) can be distinguished in the arthrosis of the hip joint:
- Initial - pathological changes are slightly expressed, provided that timely and proper treatment can be reversed.
- Progressive coxarthrosis - characterized by gradual increases in symptoms (joint pain and mobility degradation), changes in joint tissues are irreversible, but therapy can slow down degenerative processes.
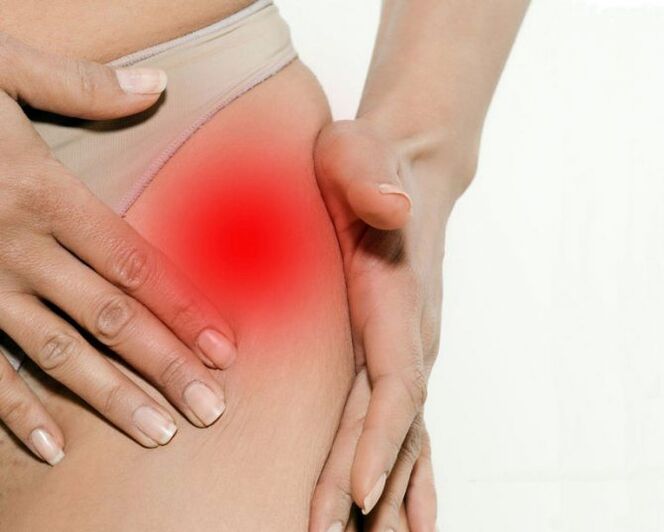
- The final movement is lost in the joint and ankylosis develops.Treatment is only possible from a surgical point of view (replacing the joint with craft).
Endoprostetics operations in 95% of cases ensure a complete restoration of the mobility of the limbs and restore the patient's performance.
Symptoms of arthrosis of the hip joint
The main signs of the hip arthrosis are:
- pain in the groin, hips and knees;
- feeling of stiffness in the affected joint and limiting mobility;
- lameness;
- Restriction of kidnapping;
- Atrophic changes in the thigh muscles.
Certain symptoms of arthrosis of the hip and their severity depend on the degree of disease.
At 1 degree of arthrosis of the hip joint, patients complain of pain in the affected joint, which occurs due to physical activity (longer walks, running).In some cases, the pain is localized in the area of the knee or thigh.After a short rest, the pain depends on itself.The volume of the limb movements remains completely, the walking is not broken.The following changes are shown in the X -ray:
- a slight uneven decrease in the lumen of the joint gap;
- Located on the inner edge of the rotating rotation.
Any change in the head of the cervical and femur is not detected.
The hip joint II.Artrosis II.After physical activity, the patient begins to soften and develops a distinctive "duck" gait.So, after a long mobility, the first few steps cause pain and discomfort, which then returns after a long load and then returns.The amount of movements in the affected joint (kidnapping, internal rotation) is limited.X -rays show that the joint gap is unevenly narrowed and is 50% of the norm.The osteophytes are located along the internal and outer edges of the joint, transcending the cartilage boundaries.The contours of the femoral head become uneven due to deformation.
The pain stump joint III.Artrosis III.The walk is very difficult, and the patient is forced to rely on the reed.The amount of movements of the affected joint is sharply limited and later stopped completely.Due to the atrophy of the hip muscles, the pelvis differs in the front plane and the limb is shortened.Trying to compensate for this shortening, while walking patients are forced to reject the body towards the injury, which further increases the load of the sore joint.Detection of X -rays, multiple bone growth, significant narrowing of joint gap and a pronounced increase in the femoral head.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of the arthrosis of the hip joint is based on the results of the clinical image of the disease, medical examinations and instrumental examinations, between which the main value belongs to the display methods - radiography, calculated or magnetic resonance imaging.These allow not only to determine the presence of arthrosis of the hip joint and to evaluate its degree, but also to determine the potential cause of the disease (trauma, youthful epiphiziolysis, Peters).
Diagnosis of arthrosis of the hip joint with other diseases and other diseases of the muscle system.II.And III.At the stage of the muscle atrophy, which can cause intense pain in the knee joint, drive or gonarthrosis (knee disease).For differential diagnosis of these conditions, the palpation of the knee and hip joints is palpable, the amount of movement is determined and they are examined from a radiological point of view.
In some cases, the nerve root of the spinal cord is stuck with the development of pain syndrome.Pain can radiate to the hip joint and imitate the clinical image of the defeat.However, the nature of radicular syndrome pain is slightly different from the arthrosis of the hip joint:
- Pain occurs as a result of weight lifting or sharp embarrassing movement, not due to physical effort;
- The pain is localized in the gluteal and not in the inguinal region.
In the case of radicular syndrome, the patient can safely reach his leg, while the arthrosis of the hip joint is limited.A typical sign of radicular syndrome is a positive symptom of tension - the appearance of sharp pain when trying to lift a straight leg on the patient's back.
The hip joint arthrosis affects people under 40 years of age, and women are repeatedly ill than men.
The joint joint of the hip joint should be distinguished by loyal bursite (Trochanteritis).Bursitis develops faster within a few weeks.Usually preceded by significant physical effort or injury.In this disease, pain is much more pronounced than arthrosis of the hip joint.However, the limb shortening and limiting mobility are not detected.
The clinical image of atypical reactive arthritis and ankylosing spondilitis may be similar to clinical manifestations of hip arthrosis.At the same time, pain occurs primarily at night or at rest, when walking does not increase, but on the contrary, weaken.In the morning, the patients take stiffness in the joints, which will disappear in a few hours.
Treatment of joint joints of the hip joint
Orthopedics are involved in the treatment of arthrosis of the hip joints.Conservative therapy is warranted with degrees I and II.In the case of pronounced pain syndrome, patients prescribe non -steroid anti -inflammatory drugs in a short course.They should not be accepted for a long time, as they can not only have a negative effect on the organs of the stomach tract, but also suppress the regeneration capabilities of hyaline cartilage.
In the treatment of arthrosis of the hip joint, they contain chondroprotectors and vasodilators, which provide optimal opportunities to restore damaged cartilage tissues.The pronounced muscle cramps may require the appointment of central muscle relaxation.
In cases where the pain syndrome can not be stopped with non -steroid anti -inflammatory drugs, the use of intraarticular injections of corticosteroids.
Topical treatment of hip joint arthrosis with heating ointments allows you to reduce muscle cramps and slightly weaken pain due to disturbing effect.
Physiotherapy methods are also used in the complex therapy of the arthrosis of the hip joint:
- magnetic therapy;
- inductothermia;
- UHF;
- laser therapy;
- ultrasound treatment;
- massage;
- medical gymnastics;
- Hand therapy.
The dietary nutrition of the arthrosis of the hip joint is aimed at repairing body weight and the normalization of metabolic processes.Reducing body weight reduces the load on the hip joints and thus slows down the progress of the disease.
To unload the affected joint, your doctor may recommend that patients go to the crutches or reeds.
The hip joint III.Artrosis III.Conservative treatment is not effective.In this case, the patient's condition can be improved, only as a result of surgical intervention can be returned to normal mobility - the destroyed joint by replace artificial (joint endoprostanism).
Possible consequences and complications
The most serious complication of the progressive arthrosis of the hip joint is disability due to the loss of joint movement.In bilateral cokertrosis, the patient loses his ability to exercise independently and needs constant foreign care.Staying in a long bed in one position creates prerequisites for stagnant (hypostatic) pneumonia, which can be difficult to fail and lead to death.
The pathology is not inherited, but the child inherits the properties of the structure of the muscle bone from their parents, which can cause arthrosis of the hip joint.
Forecast
Hip joint arthrosis is a progressive chronic disease that can only be completely cured in the early stages to eliminate the cause of the disease.In other cases, therapy allows you to slow down your orbit, but over time you need to implant hip endoprotheses.Such operations in 95% of cases completely restore the mobility of the limbs and restore the patient's performance.Modern prostheses have a life expectancy of 15-20 years and then replace them.
Prevention
Prevention of the hip joint arthrosis is to eliminate the causes that can lead to this disease and include:
- timely detection and treatment of the diseases and injuries of the hip joint;
- rejection of a sedentary lifestyle, regular but not excessive physical activity;
- body weight control;
- rational nutrition;
- Denying bad habits.